The drug enclomiphene citrate is a derivative of clomiphene citrate. Enclomiphene is a relatively new drug that is not only more effective than simple clomiphene (clomid), but also avoids many side effects of its predecessor.
Clomiphene consists of two isomers zuclomiphene (zuclomiphene) and enclomiphene (enclomiphene). Zuclomiphene is an estrogen agonist, is associated with numerous side effects, such as decreased libido, while enclomiphene has an antiestrogenic effect in the same tissues.
Encomiphene is an estrogen receptor antagonist. It blocks estrogen, causing the body to increase LH and FSH levels. This stimulates the testicles to produce more testosterone and sperm. And unlike testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), which replaces your body’s natural testosterone production with a synthetic version, enclomiphene helps your body produce more natural testosterone. This will help you avoid side effects associated with synthetic testosterone, such as shrinkage of the testicles, enlarged prostate, cardiovascular problems.
Enclomiphene can be used to increase testosterone levels, whether you have a low level or simply want to get an edge in energy, self-confidence, sexual function and athletic performance.
Mechanism of action
Enclomiphene has a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) action, which means that it interacts with estrogen receptors in the body, but has a different effect in different tissues. As a result, it may have an estrogen-blocking effect in some tissues, such as mammary glands, but not in others, such as bone tissue. This allows the use of enclomiphene to treat various conditions associated with an imbalance of estrogen in the body.
Encomiphene is a selective estrogen receptor antagonist, counteracting estrogen receptors in the pituitary gland, interrupting the negative feedback loop of estrogen in relation to the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which ultimately leads to increased secretion of gonadotropins – LH and FSH and a consequent increase in the level of testosterone circulating in the blood.
Enclomifene vs Clomifene
Clomiphene is made up of two isomers: enclomiphene and zuclomiphene.
While enclomiphene blocks the binding of estrogen to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland of the brain, zuclomiphene increases the level of estrogen and accumulates over time.
Enclomiphene is superior to clomiphene because it has fewer side effects and stays in the body for a shorter period of time.
Clomiphene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), a class of drugs that affect the production of estrogen. By blocking the production of estrogen, clomiphene “tricks” the body into thinking it is not getting enough estrogen, thereby stimulating the production of the hormones luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). In women it helps stimulate ovulation. In men, increased LH and FSH levels help stimulate testosterone production and spermatogenesis.
Despite its popularity in the treatment of low testosterone levels, some studies show that the use of clomiphene can have disadvantages, mainly due to the presence of zuclomiphene in it. Zuclomiphene has side effects that go beyond the therapeutic effect of the drug. For these reasons, the researchers concluded that because the two isomers have completely different biochemical and toxicological properties, there is “a need to develop a pure, selective estrogen receptor antagonist” for the treatment of men with low testosterone levels.
Comparing clomid with enclomiphene, researchers found that enclomiphene wins. With fewer side effects and more benefits, encomyphene is the preferred choice for safely increasing testosterone levels. Zuclomiphene has been shown to have a “harmful” effect on the male reproductive tract. In addition to a significant decrease in the size of the testes during testicular degeneration, zuclomiphene also caused the loss of Leydig cells, the absence of sperm in the seminal tubules, and a decrease in the size of the epididymis, seminal vesicles, and kidneys.
Due to its mixed estrogenic and antiestrogenic effects, clomiphene may also cause emotional regulation disorders such as mood swings and depression. This is thought to be due to an estrogenic imbalance caused by zuclomiphene staying in the body longer than enclomiphene.
Other reported side effects of clomiphene include irritability, anxiety, and decreased libido.
Hypogonadism in men
Encomiphene was developed as an alternative to testosterone for the treatment of hypogonadism in men to maintain sperm production and reduce the risk of negative side effects associated with taking testosterone. This helps restore normal testosterone levels in the body and improve sperm quality. Hypogonadism in men
Enclomiphene was developed as an alternative to testosterone for the treatment of hypogonadism in men, with the goal of maintaining sperm production and reducing the risk of negative side effects associated with testosterone use. It helps restore normal testosterone levels in the body and improve sperm quality.
Female infertility
Clomiphene can be used in combination with other drugs to stimulate ovulation in women who have trouble getting pregnant.
Estrogen-dependent diseases
Enclomiphene can be used to treat breast cancers that are estrogen-dependent. It helps reduce the level of estrogen in the body, which can slow tumor growth.
Treatment of hypogonadism
Hypogonadism is a pathological process caused by the lack of male sexual hormones, in particular testosterone, which has numerous consequences for the male body.
As you know, with a reduction in testosterone, many body functions suffer, such as fertility, and fatigue appears, muscle mass decreases, fat percentage increases, depression develops, erectile dysfunction. Most often, the level of testosterone in a man’s body begins to decline after 30 years, but the situation can be aggravated by obesity, diabetes and vascular diseases.
One of the treatment options for hypogonadism is the use of drugs from the SERM class.
During clinical trials, enclomiphene was tested on men with secondary hypogonadism. As a result of research, it was found that enclomiphene citrate increases the level of testosterone, the level of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, which is important for reproductive health, while the number of sperm does not decrease.
In men with secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, an increase in LH and FSH improves testosterone levels and sperm motility. Men with secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism have abnormally low testosterone levels due to normal low levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The biological role of these hormones is to stimulate the endogenous production of testosterone by the testes.
Enclomiphene treatment works differently than traditional testosterone replacement therapy, which replaces testosterone using an exogenous source and has a number of benefits, such as improving, rather than reducing, fertility, stimulating endogenous testosterone production , rather than introducing exogenous testosterone, which ultimately does not. lead to suppression of the production of one’s own testosterone, as well as the absence of negative effects on cholesterol and increased hematocrit levels.
Additionally, testosterone levels in those taking enclomiphene remain elevated even after treatment is stopped.
The efficacy and safety of encomyphene citrate in the treatment of male hypogonadism have been studied in several clinical trials. One such study, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism in 2014, showed that encomyphene citrate improves testosterone levels and sperm parameters in men with hypogonadism.
Another study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine in 2016 also showed that encomyphene citrate improves testosterone levels and sperm production in men with hypogonadism without significant side effects.
Although encomyphene citrate is not a first-line drug for the treatment of male hypogonadism, it can be an effective alternative treatment option for men who cannot or do not want to use testosterone.
Therapy to increase testosterone levels
Enclomiphene acts as an anti-estrogen, meaning it helps block the action of estrogen in the body. This can lead to an increase in testosterone levels not only for the treatment of low testosterone levels, but can also increase its level beyond the limits of the norm, which can give some advantages in terms of accelerated recovery after training and of increased psycho-emotional background.
An increase in testosterone levels can also lead to increased athletic performance, increased energy, some muscle mass and even increased self-confidence.
If you use enclomiphene for these purposes, during reception you will need to monitor the level of hormones such as estradiol and SHBG. An elevated level of testosterone will lead to an increase in these hormones, which can both create unwanted side effects and negate all the benefits of increased testosterone.
After 10 days of using enclomiphene, take a blood test for estradiol. When increasing it, use aromatase inhibitors such as anastrazole. You should choose the dosage and reduce the estradiol level to the middle of the norm. This should definitely be done, because high levels of estradiol can create problems with the psycho-emotional state and even a reduction in libido. If you have started to experience these phenomena while taking enclomiphene, it is time to reduce your estradiol levels. We recommend lowering it to half of the reference values, but perhaps you will feel better with the other values. These parameters are determined individually, since estrogen can suppress their production. It can improve muscle growth and increase strength.
Also, when using enclomiphene, it is necessary to monitor the level of SHBG. If this protein exceeds the upper limit of the norm, you should reduce it with the help of a remedy such as mesterolone. The fact is that a high level of this protein binds testosterone and prevents it from circulating freely in the blood and joining the androgen receptors, which also reduces the effectiveness of using enclomiphene if your goal is to increase levels of testosterone above normal limits. The dosage of proviron can be 25-50 mg per day, every other day or several times a week, depending on the level of SHBG in the blood. Higher dosages can negatively affect the level of endogenous testosterone.
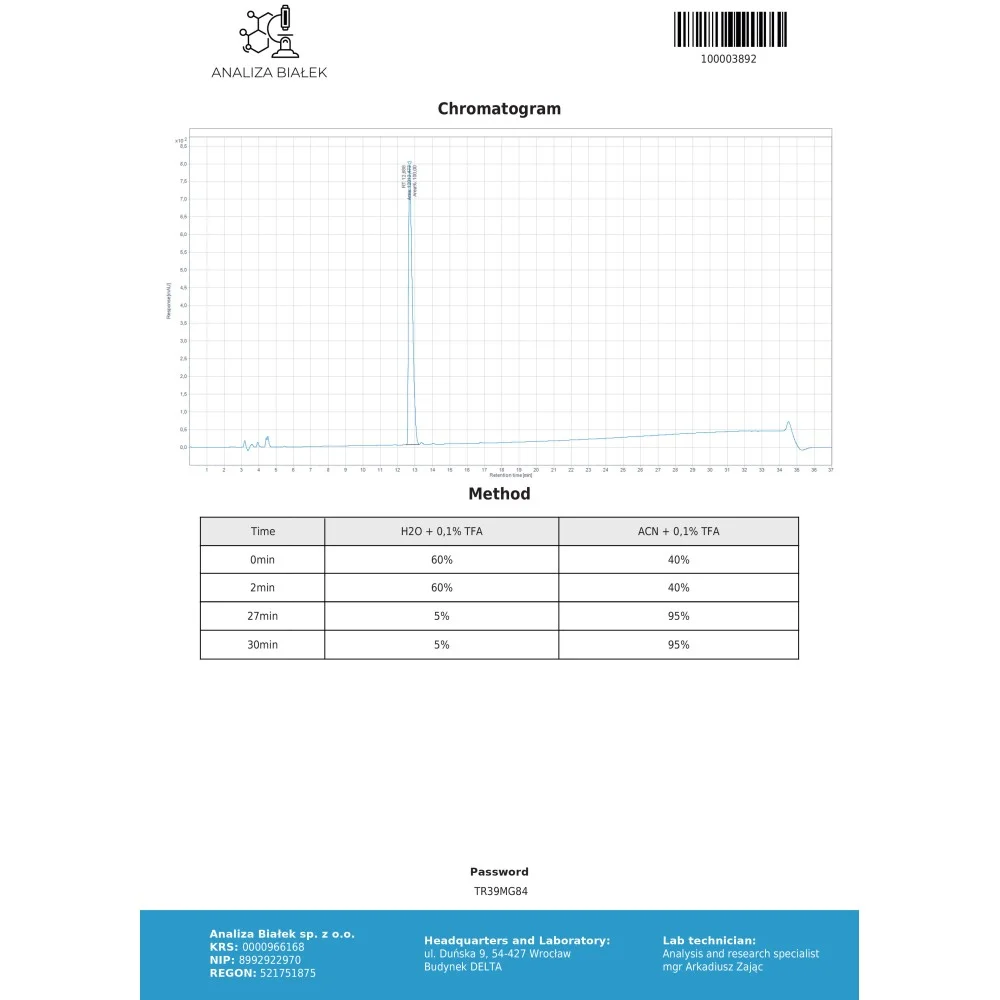
The study showed that a single dose of 12.5 mg of enclomiphene increased the testosterone level from 217.2 ng/dl to 471.9 ng/dl and allowed the testosterone concentration to be maintained high for quite a period long.
The efficacy and safety of enclomiphene citrate in the treatment of male hypogonadism have been studied in several clinical trials. One of these studies, published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism in 2014 showed that enclomiphene citrate improved testosterone levels and sperm parameters in men with hypogonadism.
Use in sports
Some studies show that enclomiphene may be effective for improving athletic performance. For example, a study published in the International Journal of Sports Medicine showed that the use of enclomiphene in men improved weightlifting results. Of course, taking enclomiphene will in no way replace a full course of anabolic steroids, but this may be an intermediate step when a novice athlete is still afraid of using AS, but already needs accelerated recovery or wants to accelerate progress a little beyond the limits of a “natural athlete”.
The use of enclomiphene for PCT
Enclomiphene can be used as a post-course therapy (PCT) drug after taking anabolic steroids. This is the effect that PED enthusiasts are most interested in. Anabolic steroids, such as testosterone, can suppress the body’s natural production of testosterone. At the end of the cycle of taking anabolic steroids, the level of testosterone in the body can be very low, which can lead to unwanted effects, such as loss of muscle mass, a decline in psycho-emotional background and a decrease in sexual function. .
Post-course therapy is aimed at restoring the natural production of testosterone in the body. Enclomiphene may be an effective drug for PCT, as it helps restore natural testosterone production by stimulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis.
Advantages
- Increases testosterone levels in both hypogonadal men and healthy men with the ability to
- Increased testosterone levels above normal limits without negative estrogenic effects that may be caused by taking its predecessor: clomiphene citrate
Dosages
The typical recommended dose of enclomiphene is 6.25-25 mg per day
Effects
Increase the level of endogenous testosterone
Side effects
- Headache
- abdominal discomfort
- Nausea
- Hot flashes
- Arthralgia
Contraindications
- Pregnant women,
- Breastfeeding women,
- wWomen with unexplained uterine bleeding
- Women with ovarian growths or cysts unrelated to PCOS
- Patients with a history of liver disease
- Patients with uncontrolled adrenal or thyroid dysfunction
- Patient with known allergy to enclomiphene or clomiphene
How to store
- Keep out of reach of children
- Store in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight
- Store at room temperature
- Do not use after the expiry date
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.